Last Updated on March 24, 2022 by Asif Iqbal Shaik
Almost a decade after the release of the world’s first 4G smartphone, the HTC Thunderbolt, we are now witnessing widespread launches of 5G smartphones from various brands. In 2019, only a few high-end smartphones had 5G connectivity built-in, and they were only launched in a few markets such as China, Europe, and the US. In India, the first set of 5G smartphones started arriving in 2020, but those were just the high-end models. This year, even mid-range smartphones released in India have 5G connectivity. But the important question remains: Should you actually buy a 5G smartphone in India right now?
Since there are no 5G networks in India right now (as of April 2021), is it wise to spend money on a 5G smartphone? To answer that question let us understand what is 5G, what are its advantages over 4G, and when we can expect 5G networks to reach your city.
What Is 5G?

A 5G network refers to the fifth-generation technology standard for mobile phone networks. It comes after 1G (First Generation), 2G (Second Generation), 3G (Third Generation), and 4G (Fourth Generation). 5G mobile networks promise data download speeds of up anywhere between 1Gbps and 10Gbps. However, real-world speeds are somewhere around 100-500Mbps.
In the following table, you can see all the telecommunication technology generations, popular technologies in those generations, when they were introduced, and what were the theoretical maximum download speeds as well as typical download speeds.
| Mobile Network Generation | Introduced | Technologies | Maximum Download Speeds | Typical Download Speeds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G | 1987 | AMPS, NMT, TACS | 2.4Kb/s | 1Kb/s |
| 2G | 1993 | GPRS, EDGE | 0.1Mb/s to 0.3Mb/s | <0.1Mb/s |
| 3G | 2001 | HSPA, HSPA+, UMTS, CDMA2000 | 0.3Mb/s to 42Mb/s | 0.1-8Mb/s |
| 4G | 2009 | LTE, WiMAX | 100Mb/s to 1Gb/s | 10-100Mb/s |
| 5G | 2018 | 5GNR (sub-6GHz, mmWave) | 1Gb/s to 10Gb/s | 100-400Mb/s (sub-6GHz) or 500Mb/s-1.8Gb/s (mmWave) |
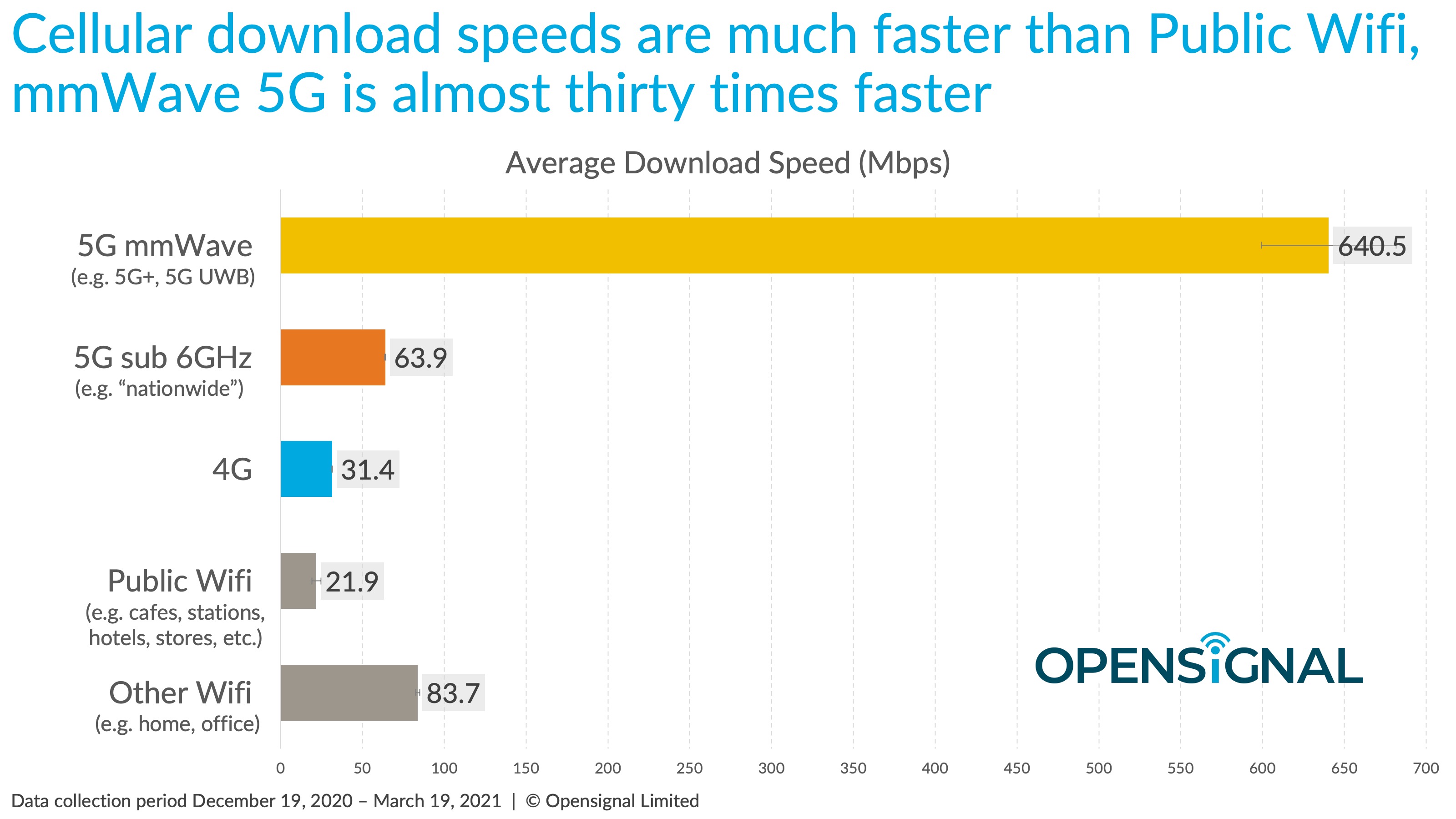
As you might have noticed in the table above, 5G download speeds vary wildly from as low as 100Mb/s to 1.8Gb/s. That is because a 5G network’s performance depends on the type of 5G used by the network carrier, real-time network load, reception quality, and the capabilities of the 5G smartphone (or any 5G capable device).
5G networks are operated based on three types of frequency bands: low-band, mid-band, and high-band.
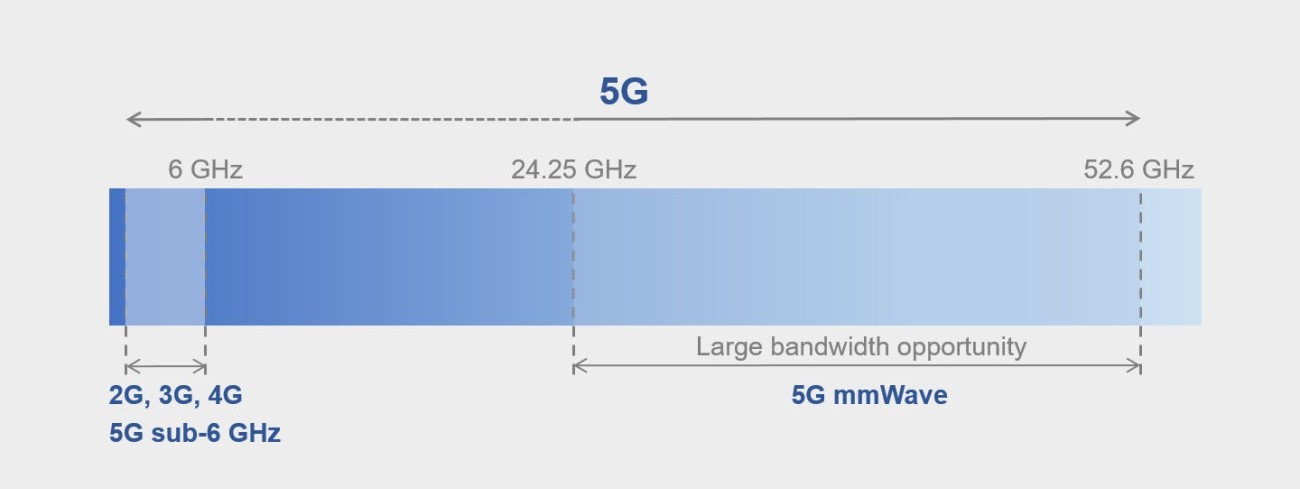
- Low-band 5G networks have an extremely long range, but the download speeds on such networks are barely faster than 4G networks. You can expect download speeds of anywhere between 20Mb/s to 250Mb/s on such low-band 5G networks. Each low-band 5G tower can offer network coverage similar to 4G networks, which means tens of kilometres.
- Mid-band 5G networks (also known as sub-6GHz) use microwaves of anywhere between 1GHz to less than 6GHz. They offer download speeds of anywhere between 100Mb/s and 1Gb/s. Each tower can cover several kilometres of range. Mid-band 5G is the most commonly deployed 5G technology all over the world because it offers the right balance of range and speed.
- High-band 5G networks (also known as mmWave or millimetre wave) use millimetre waves between 24GHz and 40GHz. A high-band or mmWave 5G network offers typical download speeds of 1Gb/s or more, but its range is extremely short, usually spanning just a couple of streets. High-band waves can be easily blocked by walls and other objects, so network carriers deploy multiple mmWave antennas spanning various cells. Due to its shorter range, mmWave 5G is usually only deployed in dense urban areas or public places such as parks, shopping streets, or stadiums.

Since 5G is a relatively new standard, it is used alongside 4G LTE. Hence, it is called 5G NSA (Non-Standalone). It means that the core of a 5G network could use 4G technologies, but with some 5G enhancements. After the 5G rollout becomes more common, network carriers will shift their core infrastructure to 5G SA (Standalone).
Who Invented 5G?

No brand single-handedly invented or developed 5G telecommunication technologies. Instead, several companies around the world contributed to developing 5G networks and mobile broadband technologies. All those brands formed an umbrella governing body called 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) that develops, maintains, and governs telecommunication technologies since the development of 2G networks.
Right now, there are several companies that develop and sell 5G radio hardware and 5G systems to mobile phone carriers. These are the most common brands that develop and sell 5G infrastructure:
- Altiostar
- Cisco Systems
- Datang Telecom/Fiberhome
- Ericsson
- Huawei
- Nokia
- Qualcomm
- Samsung
- ZTE
Out of these firms, Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, Qualcomm, and Samsung have been the preferred brands. However, Huawei has been banned by various countries, including Australia, India, EU countries, the UK, and the US due to security concerns.
What Are The Advantages Of 5G Over 4G?
5G has several advantages over 4G. For starters, 5G networks offer much faster data transfer rates compared to 4G networks. Moreover, 5G has a higher capacity compared to 4G. 5G is more efficient in spectrum usage, has lower latency, and the ecosystem is more unified when compared to 4G.
1. 5G Offers Higher Download Speeds Compared To 4G
As explained earlier, 5G networks offer typical download speeds of 100Mb/s to 400Mb/s on sub-6GHz networks and around 1Gb/s on mmWave networks. This is much faster than 10Mb/s to 50Mb/s which is usually offered by 4G networks.
Thanks to higher data transfer and download speeds, you can do things you’ve never been able to do before. That includes 4K and even 8K video streaming on your smartphone, tablet, or computer without any buffering. You can also make high-resolution video calls, play high-resolution multiplayer games via cloud gaming, and consume immersive VR content.
Since 5G offers faster data transfer between moving objects, connected and autonomous cars (or other vehicle types) can take advantage of 5G networks. Industrial IoT (Internet of Things), smart cities, and healthcare can take athe advantage of 5G as well.
2. 5G Has Lower Latency Compared To 4G
Apart from fast data download speeds, 5G also has lower latency than 4G while transferring data. It means that the time between you hitting that download button and the download actually starting is very low compared to 4G networks. This results in near-instantaneous and real-time access to data. This aspect is especially helpful in AR/VR applications, multiplayer gaming, cloud gaming, smart home and IoT controls, connected cards, and smart city applications.
3. 5G Has Higher Network Capacity Compared To 4G Networks
Since 5G has a higher network capacity compared to 4G, 5G networks can support up to 100x more traffic. It means that more devices and people can connect using a 5G network when compared to a 4G network. But this aspect of 5G should be seen as an advantage to a network carrier rather than consumers or end-users.
4. 5G Uses Radio Spectrum More Efficiently
Due to higher radio spectrum efficiency, a 5G network can deliver services to more consumers within the same resources when compared to a typical 4G network. More devices and people can simultaneously use a 5G network and other services based on 5G. However, this aspect is more helpful to a mobile network carrier rather than the end-user.
5. 5G Is A More Unified Ecosystem
Unlike 4G, 5G networks are designed to connect more than just smartphones, tablets, laptops, and PCs. The whole ecosystem was developed with keeping more use-cases in mind. It means that 5G networks can encompass not only users with smartphones, tablets, and PCs, but also industrial IoT, smart home, connected cars, autonomous vehicles, internet hotspots, and healthcare.
5G can also work alongside 4G. In fact, 5G is currently being used with 4G in the NSA mode until 5G SA becomes available. 5G also natively supports various frequency bands (low-band, mid-band, and high-band), spectrums (licensed, unlicensed, and shared), device types, and deployments (traditional cells and hotspots).
Do You Really Need To Buy A 5G Smartphone In India?

There are no 5G networks in India right now. Although Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio have already showcased live testing of 5G in India (over the existing 4G spectrum), 5G will not be launched in India anytime soon. The Indian government hasn’t even auctioned the spectrum for 5G mobile networks yet. Several reports claim that the auction of the 5G spectrum will happen in India in late 2021 or sometime in 2022.
When Will 5G Launch In India?
Once the spectrum auction completes, mobile network companies will reportedly take anywhere between six months to a year to roll out the first 5G network in India. So, we can expect 5G to launch in India towards the end of 2022 or in early 2023, given that the spectrum auction happens in early 2022. The rollout of 5G would most probably start with a handful of major cities in India. A majority of consumers across Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities and villages won’t get access to 5G networks a year or two from the first 5G rollout, which means that a majority of Indian consumers may only get access to 5G sometime in 2024 or 2025.
Should You Buy A 5G Smartphone In India Right Now?
Since you can’t use a 5G network in India right now, investing in a 5G smartphone is not wise at all. We do not recommend anyone in India to buy a smartphone only because it features 5G connectivity. Comparable 4G smartphones are anywhere between ₹3,000 to ₹7,000 cheaper when compared to 5G smartphones. However, if you are planning to buy a phone and keep it for the next three years, then investing in a 5G smartphone is okay. However, most people upgrade their smartphones once in two or three years. So, we would still recommend you to save money and upgrade to a 5G smartphone when 5G networks have actually launched in your city or locality.
Now that you know 5G is not critical in India right now, you can go ahead and buy a 4G smartphone without any hesitation or the fear of missing out on the 5G feature. Most new high-end smartphones in India, however, come with 5G connectivity by default. So, if you are buying the latest high-end smartphone from most brands, there’s a good chance of it having 5G connectivity by default. You can find the list of best smartphones in the articles listed below:
- Best high-end and foldable smartphones in India
- Best smartphones below ₹50,000 in India
- Best smartphones below ₹30,000 in India
- Best smartphones below ₹20,000 in India
Apple’s iPhone 12 series features sub-6GHz 5G in India. Samsung’s Galaxy S21 series, Galaxy Z Fold 2, and the Galaxy Note 20 Ultra feature 5G connectivity. High-end and some mid-range smartphones from ASUS, OnePlus, OPPO, Realme, Vivo, and iQOO are 5G-equipped. Even Motorola and Samsung are preparing to launch mid-range 5G smartphones in India very soon.


Discussion about this post